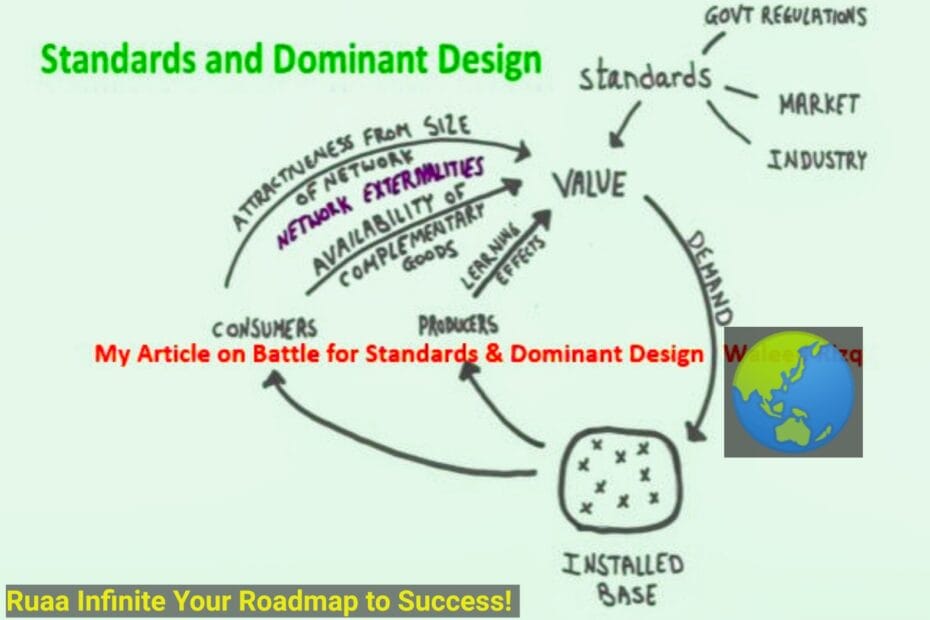
As is generally known, that a single product or process structure dominates the product segment – usually 50 percent or more of the market. This concept, known as dominant design, refers to a de facto industry standard that, while not formally enforced or recognized, becomes the benchmark within the industry.
It is evident that the market competition is tense, therefore numerous people commenced wondering, what made a new minor company such as Microsoft survives in a severe competitive market. Anyone reads its historical record realizes that the design dominate was the key factor behind its success due to many reasons. In other words, Market competition is inherently intense, prompting many to wonder how a new minor company, such as Microsoft, managed to survive and thrive in a highly competitive market. Anyone who examines its historical trajectory can see that dominant design was the key factor behind its success for several reasons:
Microsoft’s Path to Dominant Design
First: The Early Days and DOS: Looking back at the company’s history, Microsoft began as an entrepreneur-driven entity that provided an operating system for IBM’s personal computers. At that time, Microsoft was a relatively obscure company with limited market presence. However, after acquiring the rights to produce DOS, Microsoft successfully developed the operating system to meet consumer satisfaction globally. This transition was pivotal in the company’s journey toward establishing a dominant design, coinciding with the proliferation of personal computers between 1975 and 1989.
In the early stages, Microsoft’s acquisition of the DOS operating system from Seattle Computer Products and subsequent deal with IBM marked a critical turning point. This move allowed Microsoft to supply the operating system for IBM PCs, which rapidly became the industry standard. This strategic partnership not only provided Microsoft with a substantial revenue stream but also positioned it as a key player in the emerging personal computer market.
Second: Continuous Innovation with Windows XP: Microsoft continued to dominate international markets through relentless innovation. For instance, the development of Windows XP involved issuing three distinct updates: Service Pack 1 in 2003, and Service Packs 2 and 3 in 2005. These efforts were aimed at meeting the evolving needs and demands of their clients, ensuring that Microsoft’s design remained at the forefront of the industry.
The introduction of Windows XP was a significant milestone. It combined the stability of the Windows NT kernel with the user-friendly interface of Windows 95/98, appealing to both home users and businesses. The subsequent service packs addressed security vulnerabilities and added new features, which helped maintain user trust and satisfaction. This commitment to continuous improvement solidified Microsoft’s dominant position in the market.
The Emergence and Impact of Dominant Design
Before a dominant design emerges, the market often experiences a tumultuous period as companies compete with different designs, unsure of consumer preferences. Once a dominant design is established, the market often becomes a “winner-takes-all” scenario, resembling a monopoly. This means that there is a clear preference for one product design over others, driven by consumer behavior rather than purely rational decision-making.
During the pre-dominant design phase, companies experiment with various features and designs to gauge market response. This period is marked by significant uncertainty and innovation. Companies invest heavily in research and development, marketing, and strategic partnerships to gain an edge. The competition is fierce as firms strive to establish their designs as the industry standard.
Once a dominant design is established, the market dynamics shift dramatically. The winning design garners widespread adoption, creating a network effect that further entrenches its position. Competitors that failed to anticipate the dominant design must pivot quickly or risk obsolescence. This shift can lead to market consolidation, where a few dominant firms control a significant portion of the market.
Implications for Stakeholders
Consumers:
• Pros: Consumers benefit if the widespread adoption of the technology outweighs the costs associated with monopolistic practices (e.g., lower diversity, higher prices, and reduced quality).
• Cons: If the dominant design does not provide significant benefits, consumers may not prefer it, especially if the costs outweigh the advantages. One crucial factor influencing consumer demand is the product’s price.
From a consumer perspective, the emergence of a dominant design can streamline purchasing decisions and improve compatibility across different products. For example, software and hardware designed for Windows operating systems typically offer better interoperability and user experience. However, the downside includes potential price increases, reduced innovation, and limited choices.
Competitors:
• Competitors are generally at a disadvantage unless the technology is open and free to use without intellectual property restrictions. Companies that do not adopt the dominant design technology lose their investments and must play catch-up.
For competitors, the emergence of a dominant design can be both a challenge and an opportunity. On the one hand, firms that did not anticipate the dominant design face significant barriers to entry and may incur substantial losses. On the other hand, companies that align their strategies with the dominant design can leverage its widespread adoption to scale rapidly and capture market share.
Complementors and Suppliers:
• The emergence of a single dominant design can reduce the influence of suppliers and complementors while minimizing market uncertainty and the costs associated with supporting multiple technologies. Complementors can benefit from a dominant design as it prevents resource wastage on non-thriving platforms and expands the market for their products.
Complementors, such as software developers and peripheral manufacturers, often align their products with the dominant design to ensure compatibility and market acceptance. This alignment can drive innovation and reduce the risk of investing in technologies that may not gain traction. Suppliers, however, may face increased pressure to conform to the dominant design specifications, potentially reducing their bargaining power.
The Role of Product Design
Product design significantly contributes to its market attractiveness. According to Bazaar magazine, 20 percent of consumers are attracted to the product’s color, 30 percent to its shape, and 10 percent to its purpose. This highlights that the best product doesn’t always win; instead, the design plays a crucial role in consumer purchasing decisions.
The aesthetics and usability of a product can influence consumer preferences more than technical specifications. Companies invest heavily in design to differentiate their products and appeal to target demographics. For instance, the sleek design of Apple’s products has been a key factor in its market success, despite the premium pricing.
Conclusion
When a dominant design emerges, it creates opportunities for additional product classes to address unmet needs. Companies are increasingly focusing on refining their product designs to achieve dominance. The historical trajectory and path dependency also significantly influence technological outcomes, underscoring the importance of design in market success.
The battle for standards and dominant design shapes industries and determines the market leaders. Companies that understand and navigate this landscape effectively can achieve long-term success and establish themselves as industry benchmarks.
I hope my message finds you well and in good health and condition.
Have a wonderful day everyone!
Warm Regards,
AL Waleed R.
I truly appreciate this blog postThanks Again Awesome
Thank you so much for your kind words! We’re thrilled that you appreciated the blog post. Your support means a lot to us. Stay tuned for more awesome content!
Best regards,
Ruaa Infinite Team
I keep listening to the news update lecture about receiving free online grant applications so I have been looking around for the best site to get one Could you advise me please, where could i get some?
Thank you for reaching out! For information on free online grant applications, you might want to explore reputable websites such as Grants.gov, Foundation Center, or the GrantWatch platform. These sites provide comprehensive listings and resources for various grant opportunities. If you have any specific requirements or need further assistance, feel free to ask!
Best regards,
Ruaa Infinite Team
I value the blogMuch thanks again
🌟 Special for Teacher Waleed’s students! 🌟
Dear students,
Great news! 📚 You can now download the Speak Out A2 book directly from our post in Ruaa Infinite – English Students Hub:
👉 https://ruaainfinite.com/elevate-your-english-how-to-use-the-english-students-hub-for-success/
✅ Perfect to boost your speaking and listening
✅ Step-by-step practice to build your confidence
✅ Free for all Teacher Waleed’s students!
📥 Download now and start practicing today! 🔥🎤
Let’s keep learning together and make your English journey smoother and faster! 🚀✨
With best wishes,
Teacher Waleed 🌿
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://accounts.binance.com/lv/register-person?ref=SMUBFN5I
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
I don’t think the title of your enticle matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the enticle. https://accounts.binance.info/register-person?ref=IHJUI7TF